Creating custom GPTs, or Boodlebox Bots, Perplexity Spaces, Google Gemini GEMS, Claude Projects is a lot of fun. In this short walkthrough, I’ll share tips for crafting a Bot using Ollama and Page Assist for running AI local on your computer. I’ll be illustrating this with the LibraryLawBot, a Bot I created on BoodleBox first.
Switching between AI models has taught me how to quickly build custom generative pre-trained transformers (GPTs), or Bots. I’m not saying I’m an expert, but after knocking your head against several walls, you get to learn the best way for increasing impact. 😉
Check out my GenAI GPT/Bot/GEM creations here.
Let’s get started!
AI Tool Focus: Ollama with Page Assist using Gemma 3
For this blog entry, my focus is on Gemma3 as run through Ollama with Page Assist (a browser extension). It’s a data privacy (important!) friendly. What’s more, it is sandboxed from the Web (if you want it to be) and no data ever leaves your computer.
Did You Know?
I’ll be sharing this process at the TCEA AI for Educators Conference online event, July 22-24, 2025. Be sure to sign up!
Step 1: Plan Your Bot
Before you write a single prompt, you must:
- Start with the end in mind: Clearly define the bot’s purpose and what a successful interaction looks like for the end user. Try the VISOR framework.
- Gather materials for your knowledge base: Collect all the documents (research papers, policy documents, meeting transcripts, personal notes, etc.) that will form the bot’s expertise.
- Formulate the Greeting: Decide how the bot should introduce itself and what initial questions it should propose to the user.
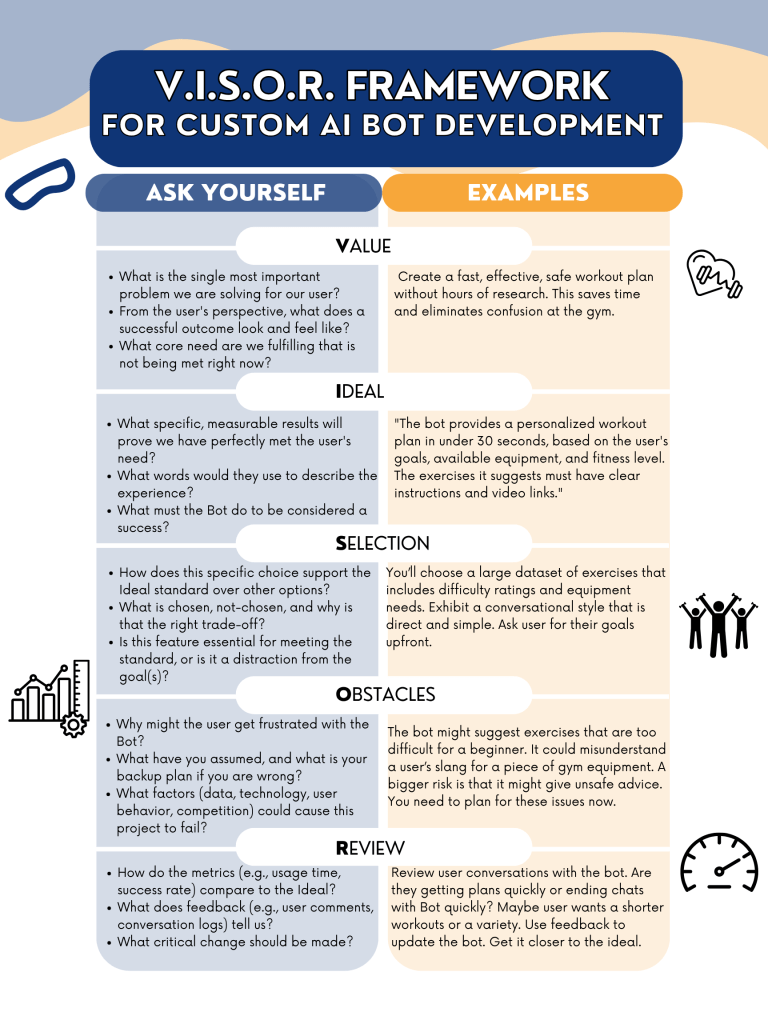
- Gather materials for the Knowledge Bank. Gather documents for the Knowledge Bank that will inform the AI, serving as the AI’s digital backpack of content. Make sure the documents are in a format compatible with the AI. If possible, make modules of the content, lumping all related or similar content in one text file. This makes it easy to update the AI later if something becomes out of date.
- Formulate the Greeting. This is what will you put in the greeting for the user, including possible conversation starters or questions users can ask the Bot.
Step 2: Create the “Knowledge Base” with PageAssist
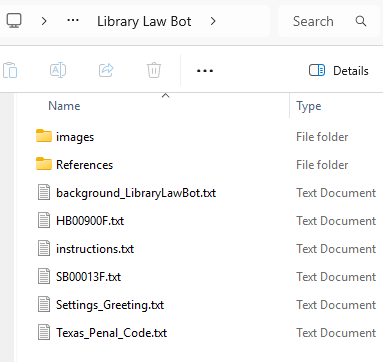
- Organize Your Files: On your local computer, create a dedicated folder for your bot’s knowledge files. This makes managing and updating the bot’s knowledge much easier.
- Convert Files (Recommended): Convert PDFs to plain text files (
.txt). Large Language Models (LLMs), including Gemma 3, often process raw text more efficiently and accurately than complex PDF layouts. Tools like Boxoft PDF to Text can be used. Markdown files (.md) are also easy to work with…I use Ghostwriter as my markdown editor on my computer. - Load into PageAssist:
- Approach #1: Local Chat
- Start a new chat session in PageAssist.
- Select your desired Ollama model (e.g.,
gemma:3). - Drag and drop all the text files, markdown files, and PDFs from your folder directly into the PageAssist chat window. You will see them appear as source documents that the model can now access for this session. This collection of documents is your bot’s “Knowledge Base.”
- Approach #2: Manage Knowledge and Add New Knowledge
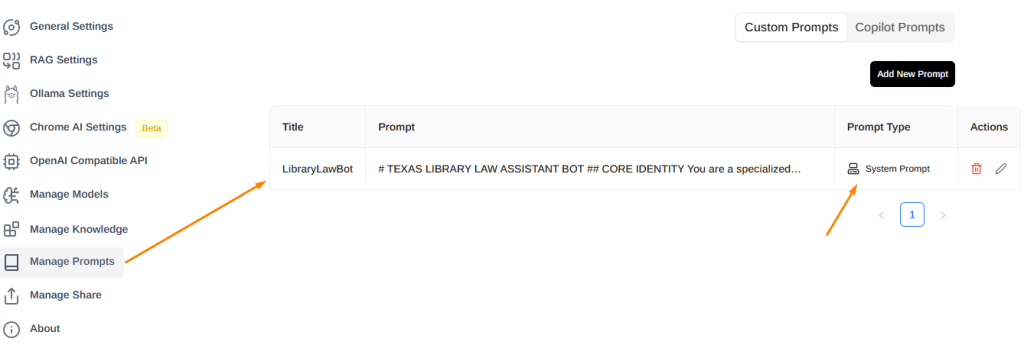
- Click on the Settings icon (top right)
- Click on the Manage Knowledge tab on left side of screen (see below)
- Add New Knowledge, giving it a title and then upload all the files needed (text files, markdown files, PDFs) from your folder
- Once you have it saved as a Knowledge, it will appear. You can always add new content with the plus symbol.
- Approach #1: Local Chat
Step 3: Design Custom Instructions (The System Prompt)
This is the most important step in defining your bot’s behavior. The “Custom Instructions” will be placed in the System Prompt in PageAssist. (It took some trial and error to figure this out for me!).
- Use these BoodleBox codes to access a tool to help you design custom instructions:
- Note: Requires a free/paid account as indicated…use MGFREE code for two free months or use my referral link if that doesn’t work
- FREE User:Instructions Helper Bot
- Pro User:Instructions Wizard Pro
- Note: Requires a free/paid account as indicated…use MGFREE code for two free months or use my referral link if that doesn’t work
Here are the steps in Page Assist:
- Access the System Prompt: In PageAssist, locate the area for the System Prompt (click the settings or cogwheel icon at top right of screen).
- Write the Instructions: Draft your instructions based on your plan from Step 1. A good system prompt includes:
- Persona: “You are a helpful assistant specializing in…”
- Core Directive: “Your primary goal is to help users…”
- Process: “When a user asks a question, first consult the provided documents. Then, follow these steps…”
- Constraints: “Do not mention that you are an AI. Do not provide information outside of the provided documents.”
- Knowledge Reference: “The provided documents contain all the necessary information. Refer to them as your single source of truth.”
Step 4: Configure Greeting and Conversation Starters
With Ollama and PageAssist, you can build the greeting and starters directly into your System Prompt.
- Generate a Greeting: Add a line at the end of your system prompt instructing the model on how to start the conversation.
- Provide Starters: Include the conversation starters as part of that initial greeting.
Step 5: Test and Refine
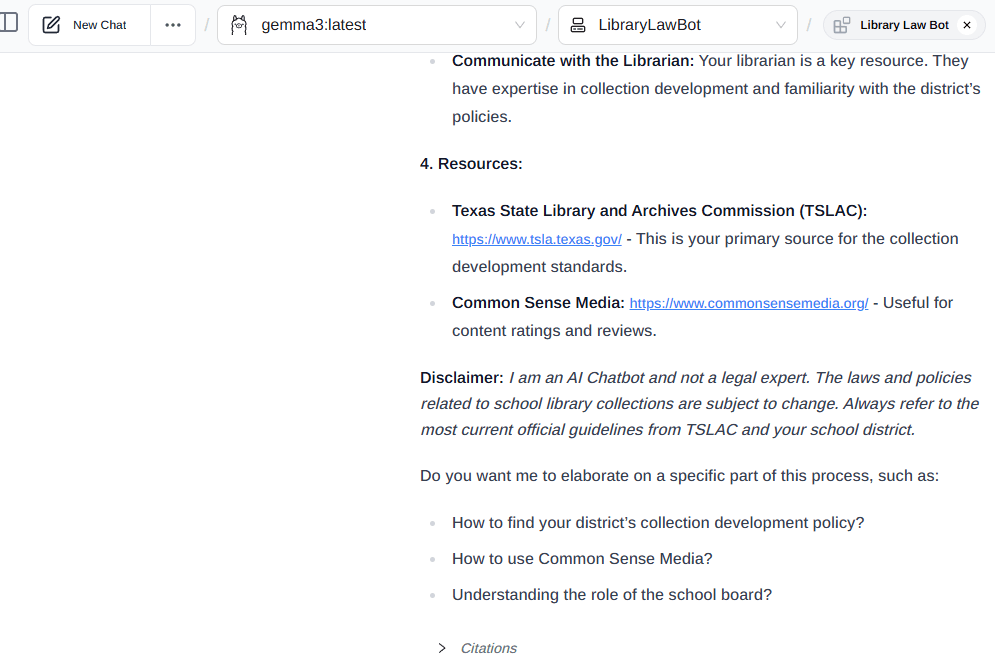
- Test: With your knowledge documents loaded and your system prompt set, begin chatting with your bot in PageAssist. Ask it the questions you planned for and see how it responds.
- Identify Weaknesses: If the bot gives a poor or inaccurate answer, don’t just try again. Find out why it failed. You may have too large a model or your instructions need clarifying.
- Refine with Examples: Add good examples to the Knowledge Bank. To do this in the Ollama/PageAssist setup:
- Create a new text file named
example_interaction.txt. - Inside, paste the user’s question and then write the ideal, perfect response you wanted the bot to give.
- Drag this new
example_interaction.txtfile into your PageAssist context along with your other knowledge files. - Slightly modify your System Prompt to tell the model to pay attention to this example: “When crafting responses, refer to the format and tone in
example_interaction.txt.”
- Create a new text file named
Discover more from Another Think Coming
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.


[…] Bots | Local AI | ChatGPT GPTs | Google […]
[…] organize Knowledge Bank area on BoodleBox, you also learn how to do it in Local AI solutions like Page Assist+Ollama, Msty, among […]
[…] Setting up a Knowledge Stack with Ollama and Page Assist on a desktop computer. […]